What is Air Pollution?
This refers to the contamination of the air by harmful substances, including gases, particulates, and biological molecules, which can negatively impact human health, the environment, and climate. This guide will equip you with the knowledge to understand what pollution is, its causes, effects. Let’s take a deep breath (hopefully clean air!) and dive in.
Key Takeaways Upfront:
- Beyond Smog: It isn’t just about thick, gray smog. It encompasses a variety of harmful gases, particles, and even biological agents that contaminate the air.
- A Multitude of Sources: From vehicle emissions to industrial processes and even natural phenomena, the culprits behind pollution are numerous and varied.
- A Silent Threat to Health: It doesn’t just make you cough; it can trigger respiratory illnesses, heart disease, and even cancer.
- Prevention is Key: From individual choices to collective action, there are ways to reduce pollution and safeguard our lungs (and the planet’s).
- Knowledge is Power: Understanding how air pollution is measured and monitored empowers you to make informed decisions about your health and environment.
Unveiling the Culprits: Types of Air Pollution
It is not just a single substance responsible but it’s a team of unwanted guests in our atmosphere. Here are the main types:
- Gases: These include harmful gases like nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, and ground-level ozone, often produced by vehicles and industrial activities.
- Particulate Matter (PM): These are tiny particles like dust, soot, and smoke that can penetrate deep into our lungs. PM comes from vehicle exhaust, factories, and even wildfires.
- Biological Agents: Mold spores, pollen, and even bacteria can be airborne, triggering allergies and respiratory problems.
| Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Gases | Harmful gases impacting air quality | Nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, ground-level ozone |
| Particulate Matter (PM) | Tiny particles impacting lung health | Dust, soot, smoke |
| Biological Agents | Airborne allergens and irritants | Mold spores, pollen, bacteria |
Did you know? The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 99% of the global population breathes polluted air [1]. That’s a staggering statistic, highlighting the need for action.
The Unseen Threat: Causes of Air Pollution
The sources of air pollution are diverse, and understanding them is crucial for finding solutions. Here are some major culprits:
- Vehicle Emissions: Cars, trucks, and other vehicles release harmful gases and particulate matter through exhaust fumes.
- Industrial Processes: Factories and manufacturing plants can emit a range of pollutants, depending on the industry.
- Fossil Fuel Burning: Burning coal, oil, and natural gas for electricity and cooking releases pollutants into the air.
- Agricultural Activities: Burning agricultural waste, applying fertilizers, and raising livestock can all contribute to pollution.
- Natural Sources: Forest fires, volcanic eruptions, and dust storms can also release pollutants into the atmosphere.
Beyond the Obvious: Even seemingly harmless activities like using fireplaces and wood-burning stoves can contribute to pollution, especially in densely populated areas.
The Silent Infiltrator: Effects of Air Pollution
Pollution isn’t just an eyesore; it’s a silent threat to our health and well-being. Here are some of its concerning effects:
- Respiratory Problems: Exposure to pollution can worsen asthma, trigger chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and increase the risk of respiratory infections.
- Heart Disease: Air pollutants can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Cancer: Long-term exposure to pollution has been linked to an increased risk of lung cancer and other cancers.
- Impact on Children: It can hinder children’s lung development and increase their risk of respiratory illnesses.
A Cause for Global Concern: Pollution not only impacts human health but also affects the environment. It contributes to climate change, acid rain, and disrupts ecosystems.
According to IQAir, a world leader in air pollution monitoring and solutions provider. The most polluted cities as of January 2025 are as follows.
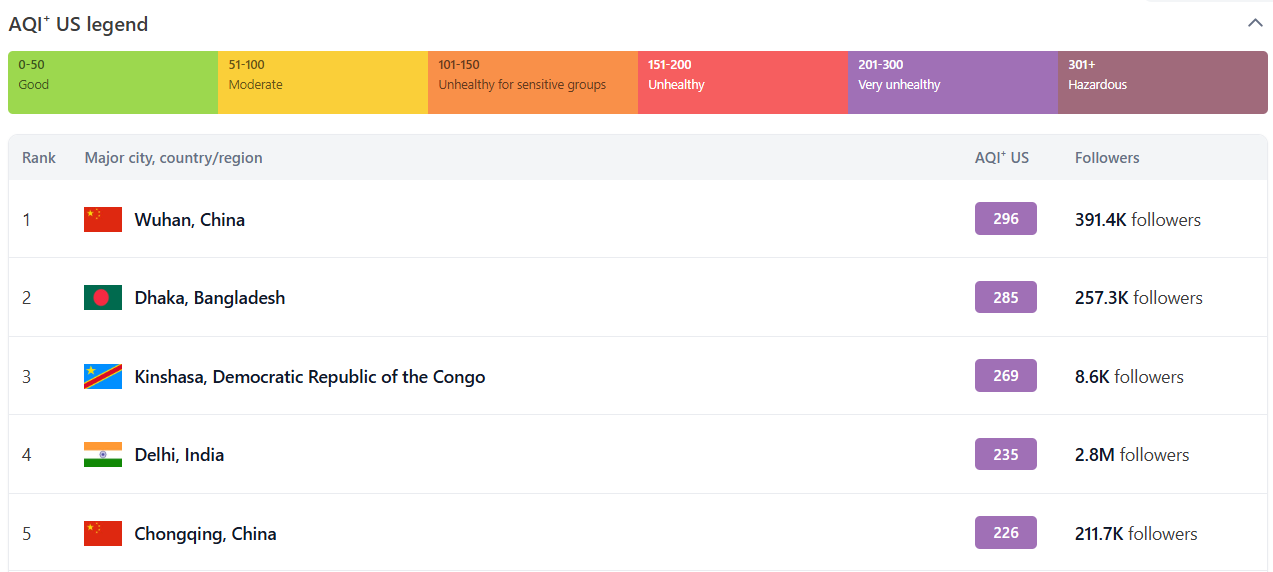
The most cleanest cities as of January 2025 are as follows.
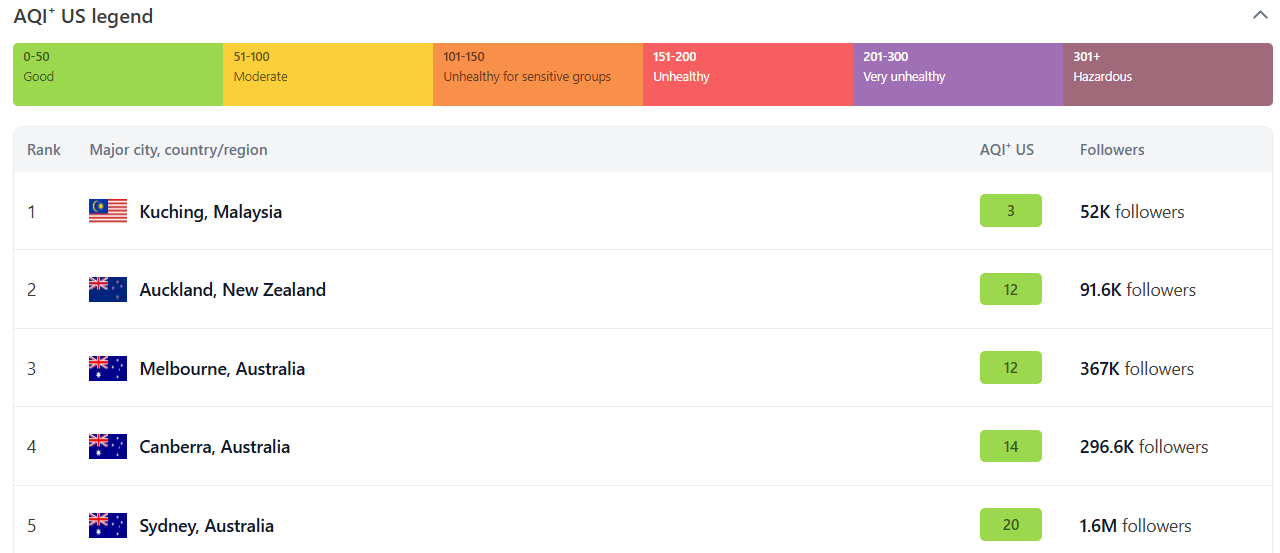
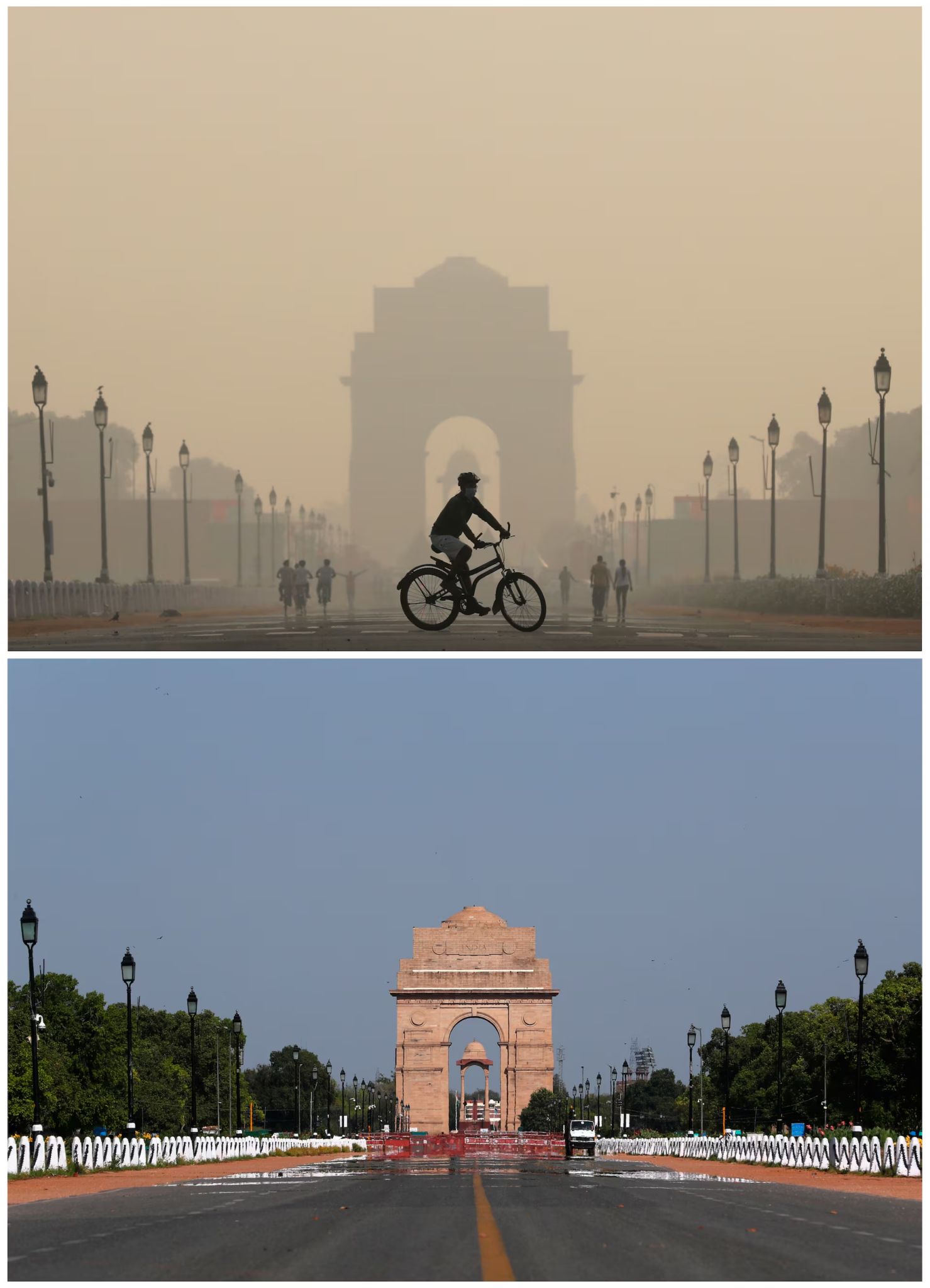
During the COVID-19 pandemic, global air pollution experienced significant reductions due to widespread lockdowns and restrictions on economic activities. As countries enforced measures to curb the virus’s spread, billions of people were confined to their homes, leading to a dramatic drop in emissions from transportation and industrial sources.

Stay tuned! In the next sections, we’ll explore ways to measure pollution and delve into valuable resources like air quality indexes and pollution maps.


Leave a Reply